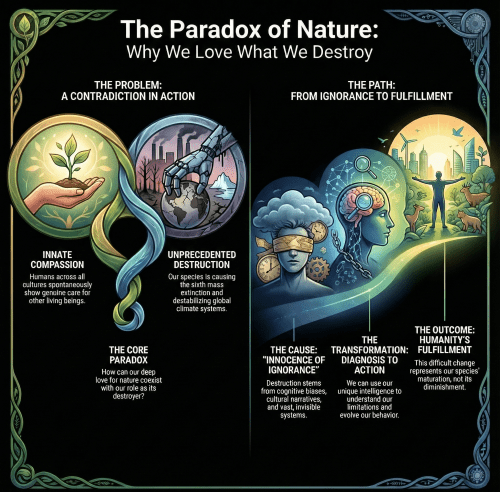
Three principles define the shift from adolescence to maturity, from destroyer to steward.
Ecocentricity means rejecting the view that nature exists for human utility. It means recognizing intrinsic value throughout the biosphere. Rivers have worth independent of irrigation potential. Forests matter beyond timber value. Species deserve protection not for ecosystem services but because they exist. New Zealand’s Whanganui River, granted legal personhood in 2017, embodies this principle in law.
Interdependence means acknowledging that no organism exists alone. The illusion of independence proves strong in urban societies, where food appears in supermarkets and water flows from taps. Ecology shows this illusion is fiction. Every organism depends on countless others. Human wellbeing requires biosphere wellbeing.
Reciprocity means moving from extraction to exchange. Industrial civilization takes resources, produces goods, and discards waste while the biosphere receives nothing in return except degradation. Reciprocity asks not only what we can extract but what we can contribute to ecosystem health. This is partnership, not parasitism.
Together, these principles transform the human-biosphere relationship from exploitation to citizenship.
[Read the full essay here.]
[Read the series introduction and access all nine essays here.]
[Donate]