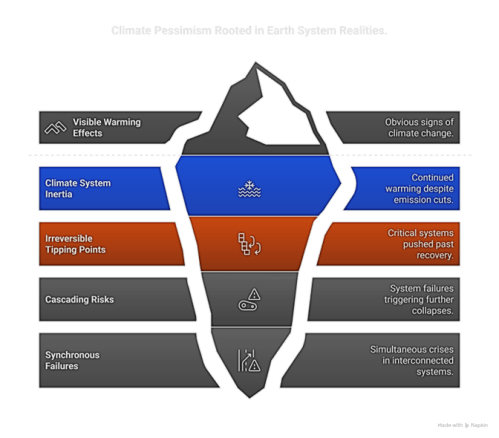
When I started writing fiction, I read books, articles, blog posts, and Internet commentaries on writing techniques. I joined local writer groups and writing circles, and I followed hundreds of writers and groups on the Internet. I created an elaborate backstory for a world like Earth except that human-like intelligence was always present in all higher organisms. After I published the first novels, I repeated what I had learned about writing in blog posts and school lectures and learned even more from readers and writers. Recently, I started compiling a series of methods books that would bring the techniques together in focused narratives. I began with a general guide (“Writer’s Primer”). Then, acknowledging AFOSA’s focus on nature conservation, I assembled a methods booklet for nature writing (“Life on Land”). After that, I began on genre methods booklets. One of them covers romance short stories. To taste my own medicine, I decided to practice romance short story techniques with a series of stories about a romance set amidst our climate-change disaster. This is the first story.
Fire Season: Love in the Time of Climate Change
Francis Ralph Graham
First Smoke (Summer 2023)
The coffee maker in the university geography department sputtered its last drops as Mia Allen checked her watch. Eight forty-seven on a Tuesday morning in late May, and she was running behind schedule for what Professor Martinez had called “the most important meeting of your graduate career.” Her hands trembled slightly as she reached for her backpack—too much caffeine, not enough breakfast, and the weight of knowing this interview could determine whether her summer comprised meaningful fieldwork or scrambling for a last-minute retail job.
The department secretary, Mrs. Chen, looked up from sorting mail with the patient smile that suggested she’d witnessed countless nervous students over her thirty years behind that desk. Her fingers moved through envelopes with practiced efficiency, separating the urgent federal correspondence from routine university mail—each envelope representing someone’s career trajectory.
“Deep breaths, dear. Dr. Martinez doesn’t bite, despite what the undergraduates claim.” Mrs. Chen paused, holding up a thick envelope marked with the Bureau of Land Management logo. “Though I suppose you’re more worried about the BLM position than facing Ricardo.”
Mia nodded, throat too tight for words. Two years of coursework in biogeography, climatology, and land-use analysis had led to this moment. Through the department’s windows, she could see maintenance crews already watering the campus landscaping despite the early hour—drought restrictions meant only morning irrigation was permitted.
The hallway stretched before her, lined with bulletin boards displaying conference announcements and research opportunities. A faded poster from last year’s American Association of Geographers meeting caught her eye: Climate Change Adaptation in Western Rangelands. The photograph showed cracked earth and struggling sagebrush beneath an impossibly blue sky, edges curling where tape had lost its grip to repeated temperature fluctuations.
Dr. Martinez’s office door stood slightly ajar, voices drifting through the gap. Mia recognized her advisor’s accented English mixed with another voice—deeper, more hesitant. She knocked twice and waited, hearing her pulse in her ears.
“Come in, come in.” Dr. Martinez gestured toward an empty chair beside another student, a young man with sun-lightened brown hair and calloused hands that spoke of work beyond classroom walls. His worn boots showed scuff marks that suggested actual field experience rather than fashion choices.
“Mia Allen, meet Samuel Powell. You’ll be working together this summer if everything goes according to plan.”
Samuel—Sam, she corrected herself after catching his quick grimace at the formal name—half-rose from his chair. When he extended his hand, she noticed the constellation of small scars across his knuckles, evidence of outdoor labor. His palm was warm and surprisingly gentle for its obvious strength, the contact lasting a moment longer than strictly professional courtesy required.
“Sam’s thesis examines post-fire invasive species succession,” Dr. Martinez continued, settling behind his desk with the measured movements of someone who’d conducted hundreds of these meetings. Papers rustled as he organized their files, each sound sharp in the morning quiet. “Your livestock grazing research complements his work perfectly. Both projects examine human-induced vegetation changes, though from different angles.”
Mia studied Sam’s profile as he turned toward their advisor. Something in his posture suggested complete focus, the intensity of someone who’d fought for this opportunity. His clothes—faded jeans, a button-down shirt that had seen better days—reminded her of home, of the practical approach to life that came from understanding consequences.
A siren wailed in the distance, growing louder before fading toward the hospital. Sam’s shoulders tensed momentarily at the sound, an unconscious reaction that made Mia wonder what experiences had shaped that response.
“The BLM district office has requested two graduate assistants for the summer,” Dr. Martinez continued, his voice cutting through the external noise. “They’re facing unprecedented challenges this fire season. Three major blazes already, and we’re barely into June. Early snowmelt, record-breaking spring temperatures, fuel moisture content approaching critical levels two months ahead of typical patterns.”
Through the office window, Mia could see students moving between classes with the unhurried pace of those whose biggest worry was upcoming finals. The contrast struck her—here they sat discussing real-world crises while twenty feet away someone complained loudly about a broken vending machine.
“The positions involve split duties,” Dr. Martinez said, pulling out two thick folders. The paper stock felt substantial, official in a way that made Mia’s pulse quicken. “Mia, you’ll work primarily with the land-use planning office under Diana Walsh. Expect long days reviewing grazing permits, conducting field surveys, learning how policy translates to ground-truth conditions.”
He handed her a folder marked with the Bureau’s logo, its weight representing months of preparation condensed into a single opportunity. Sam received his folder with similar reverence, though she noticed his thumb worrying the corner as Dr. Martinez spoke.
“Sam, you’ll be assigned to fire dispatch operations under Jack Morrison. Real-time decision making, resource allocation, communications coordination. Some office work, yes, but during active fires, you’ll be gathering information that directly affects firefighter safety.”
The weight of actual responsibility settled between them like shared understanding. This wasn’t academic theory—their analysis and recommendations would affect real landscapes, real livelihoods, potentially real lives.
Dr. Martinez leaned forward, his expression growing serious. “Dr. Hoffman will conduct your final interviews this afternoon. She’s worked with BLM for fifteen years and knows exactly what they need. Be prepared to discuss your research and your field experience.”
Mia’s stomach tightened. Field experience meant the required summer mapping course and various research trips, but nothing approaching the intensity Dr. Martinez described. She glanced at Sam, wondering if his confidence came from more extensive outdoor work or if he was simply better at hiding nervousness.
“Questions before you prepare for this afternoon?”
Sam cleared his throat, the sound rough. “Dr. Martinez, the fire assignment—what will I be doing?” He paused, fingers drumming once against his chair arm before stilling.
“Jack Morrison runs one of the safest operations in the region,” Dr. Martinez replied. “You won’t be fighting fires, Sam. Your job is information gathering and communication. But you’ll be close enough to understand why this work matters.”
Outside, another siren began its urgent wail, this one heading toward the mountains where smoke had been visible yesterday evening. Both students turned toward the window instinctively.
“Both of you will,” Dr. Martinez finished.
They left the office together, walking down the hallway as other students hurried past with the energy of those anticipating summer break. Mia felt suspended between her old life as a graduate student and whatever was coming next. The fluorescent lighting seemed harsh after the windows in Dr. Martinez’s office, artificial and insufficient.
“Coffee?” Sam asked as they reached the main lobby, then immediately looked uncertain. “I mean, if you want to compare notes before the interview. I know nothing about Dr. Hoffman except that she apparently reduces grown graduate students to tears during field methods.”
Mia laughed despite her nervousness, the sound echoing off the lobby’s hard surfaces. “I survived her Introduction to Soil Science course. Barely. She has this way of asking questions that makes you wonder if you know anything.”
The student union’s coffee shop bustled with end-of-semester energy. They found a small table near the windows, settling across from each other and the folders Dr. Martinez had given them. Around them, conversations flowed with summer plans, internships, and the universal student concerns for finals week stress.
Sam opened his folder, immediately closing it again. His fingers drummed against the table surface—a nervous habit, she realized. “So,” he said, “livestock grazing research. That sounds like you actually know what you’re doing in the field.”
“My family runs cattle,” Mia said, surprising herself with the admission. She usually downplayed her agricultural background among academics who sometimes viewed practical experience with suspicion. “Small operation compared to most in the west, but I grew up understanding how livestock interact with landscape.” She paused, remembering last summer’s drought conditions. “What remains of landscape, anyway.”
Sam’s expression shifted with recognition. “Similar background. My dad grows corn and soybeans in Iowa, but I spent summers working construction to pay for school. Hand-built fencing, erosion control projects.” He looked down at his palms, evidence of that labor written in callused skin. “Got interested in fire behavior after watching a grassland burn near our place three years ago. The way invasive species moved in afterward—like they were waiting for the opportunity.”
Something in his voice made Mia study his face more carefully. He spoke about fire with personal understanding, not just academic interest.
“That must have been intense,” she said.
“Changed everything I thought I knew about landscape stability,” Sam replied, his coffee forgotten as he leaned forward. “Made me realize that our assumptions on ecosystem recovery might be outdated. Climate may be changing too fast.”
The weight of that observation settled between them. Mia had reached similar uncertainty through her own research, watching native grasses struggle to reestablish after cattle grazing. Her father’s weathered face came to mind—the quiet frustration with agricultural extension recommendations that failed to address the flash droughts becoming commonplace.
Through the coffee shop windows, she could see acampus maintenance crew removing a sprinkler system. They moved with practiced efficiency, working with the drought limitations that now shaped every decision.
“Dr. Martinez mentioned this is an unprecedented fire season,” she said, flipping through her folder’s contents. Maps showed burn scars scattered across the western landscape like broken glass, some representing devastated communities and all displaced wildlife. “Three major fires already.”
“It hasn’t rained or snowed since February this year,” Sam said, looking at a climate summary in his materials. “The snowpack is thirty percent below normal, spring temperatures are averaging four degrees above the twenty-year normal. Fuel moisture content is at critical levels two months ahead of typical fire season.”
They studied the documents, occasionally sharing striking statistics or revealing maps. Mia appreciated Sam’s methodical approach—he was connecting the data without jumping to conclusions. His marginal notes revealed serious intent to understand the information.
A group of undergraduates at the next table erupted in laughter about their summer beach plans, the sound jarring against the data spread before them. Sam glanced over, his expression thoughtful rather than annoyed.
“Listen,” Mia said after they’d spent twenty minutes absorbed in climate data and fire projections, “I know we’re technically competing for these positions, but would you want to study together for the interview? Dr. Hoffman’s questions are notoriously unpredictable, but maybe we can prepare for the basics.”
Sam’s smile brightened his entire face, revealing warmth that had been hidden beneath interview nervousness. “Absolutely. Two perspectives are better than one, especially when facing an interrogation.”
She felt her own face flush with unexpected pleasure at his enthusiasm. The reaction surprised her—when had she started wanting his company?
They spent the next three hours testing each other on fire behavior principles, grazing impact assessments, and land-use policy frameworks. Sam’s knowledge of meteorological factors impressed Mia, while her understanding of soil science and vegetation dynamics filled gaps in his preparation.
The afternoon light shifted as they worked, shadows drifting across their shared table. Occasionally, their hands would brush when reaching for the same document, each contact creating a small electric moment that neither acknowledged but both noticed.
“You know,” Sam said during a break in their review session, “this feels more like collaboration than competition.”
“Maybe that’s what’s needed,” Mia replied. “The environmental challenges are too complex for individual perspectives.”
Something in her voice made him look up from his notes, meeting her eyes directly. The library’s quiet hum surrounded them—keyboards clicking, pages turning, the distant conversation of other students wrestling with their own academic challenges.
“After this morning,” Sam said quietly, “I’m hoping we both get selected.”
By the time they walked toward Dr. Hoffman’s office for their interviews, they moved in a private energy field along a hallway that seemed longer than usual.
“Good luck,” Mia said as they stood outside the professor’s door.
“You too,” Sam replied. He hesitated, then reached out to briefly squeeze her shoulder. The contact was warm and reassuring, lasting just long enough without crossing any boundaries.
Dr. Hoffman’s interview proved as challenging as expected. She grilled them on technical knowledge and field experience. When she asked Mia to describe how she would change traditional grazing management practices in response to climate change, the answer flowed from months of study, a lifetime of familiarity, and new perspectives added by Sam.
“Interesting,” Dr. Hoffman said, making notes. Her pen scratched against paper with decisive strokes. “And how would you respond if local ranchers disagreed with your recommendations? These are people whose families have worked the same land for generations.”
Mia recalled her father’s conversations with neighbors, the shared concerns the sense of cooperation.
“I’d start by listening,” she said. “Ranchers have generational knowledge on their specific landscapes. My job would be synthesizing that local expertise with broader research findings, looking for solutions that work both ecologically and culturally.”
Dr. Hoffman’s expression revealed nothing, but she nodded before dismissing Mia to wait in the hallway.
Sam emerged from his interview thirty minutes later, looking drained but cautiously optimistic. They walked together toward the parking lot, not willing to speculate on outcomes.
The late afternoon heat hit them as they stepped outside, carrying the scent of stressed vegetation and distant smoke. The campus trees showed signs of moisture stress, some leaves already curling despite the early date.
“Regardless of what happens,” Sam said as they reached Mia’s car, “today was valuable. I learned more in those three hours studying with you than I did in weeks of solo preparation.”
“Same here,” Mia replied firmly.
Her car’s interior was hot despite being parked in shade. She started the engine and rolled her window down, grateful for air conditioning while noting the irony of burning fossil fuels to escape heat intensified by climate change.
“Maybe we could keep in touch regardless of the BLM outcome,” she said. “Compare notes on our research?”
“I’d like that,” Sam said, then hesitated, as if considering whether to say more. The parking lot’s asphalt shimmered with heat waves, distorting the surrounding air. “Actually, I was wondering if you’d want to grab dinner sometime. Not just about the interviews or research. I enjoyed spending time with you today.”
The invitation hung between them, and Mia studied Sam’s face, noting how he calmly waited for her response, despite the hope clearly visible in his expression.
“Yes,” she said, surprising herself with the certainty in her voice. “I’d like that.”
They exchanged phone numbers, fingers brushing as he handed back her phone. The contact sent warmth up her arm, and a surprising physical awareness.
Dr. Hoffman called two days later with news that both students had been selected for the BLM positions. They would report to the district office in three weeks, after completing final exams and defending their thesis proposals.
“Congratulations,” Dr. Hoffman said, her usually stern voice carrying a note of warmth. “But understand what you’re signing up for. Climate change is accelerating faster than our institutional responses. You’ll be learning in real-time how to adapt management practices to conditions we’ve never faced before.”
That evening, Sam called to share the news and suggest a celebration dinner.
They met at a small restaurant near campus, the kind of place that attracted graduate students with generous portions and reasonable prices. They leaned together, charged with the energy of shared success and the opportunity to explore new ideas.
“Part of me is frightened,” Mia admitted over dessert, watching Sam’s hands as he gestured while talking. His fingers moved with unconscious grace, and she wondered what those hands would feel like cupping her face. “What happens to the management of grazing impacts and vegetation dynamics, when conditions are constantly changing?”
“I keep thinking about that grassland fire I witnessed,” Sam said, his voice growing quiet. “How quickly everything is becoming irrelevant. But that’s also why this work matters. We need to acknowledge the changes and adapt.”
The restaurant’s windows showed the last light of an early summer evening, sunset colors muted by atmospheric haze. Other diners filled the room with conversations concerning summer plans and job prospects, their voices creating a backdrop of normalcy unnatural beneath the weight of environmental crisis.
“Can I ask you something?” Sam said as they prepared to leave. “What made you switch from agricultural economics to geography? I mean, with your family background, the economics track seems like a natural fit.”
Mia considered the question, thinking back to the moment her academic focus had shifted. “Three years ago, during a severe drought, I watched my dad make hard decisions on which pastures to rest, which cattle to sell, uncertain if he could keep the operation viable. The economic models I was learning didn’t account for directional environmental change. They assumed there was a stable baseline that might no longer exist.”
She paused, remembering her father’s weathered face as he studied dying grassland, his quiet frustration with agricultural extension recommendations that failed to address the flash droughts becoming routine.
“I realized I needed to understand the physical systems first—how landscapes actually function under stress—before economics could provide useful guidance. You can’t develop sustainable economic models for systems you don’t comprehend.”
Sam nodded slowly, his coffee cup forgotten in his hands. “That makes perfect sense. For me, it was watching how quickly invasive species colonized the burned area. Traditional ideas about primary and secondary succession didn’t apply. Made me wonder how we were entering some new condition rather than a normal fluctuation.”
They parted that evening with plans to stay in touch throughout the rest of the semester. As Mia drove home, she caught herself anticipating Sam’s texts about his research with enthusiasm that extended well beyond professional interest.
Three weeks later, they met at the BLM district office, a low building surrounded by vehicles equipped for fieldwork and serious operational responsibilities. The parking lot’s asphalt radiated heat waves despite the early morning hour, and the surrounding landscape showed obvious stress from prolonged drought conditions.
Diana Walsh, Mia’s supervisor, was in her forties with graying hair pulled back in a practical ponytail and hands that showed decades of outdoor work. She greeted Mia with a firm handshake and an appraising look.
“Hope you’re ready to dive in,” Diana said, leading Mia toward the land-use planning office. Her stride was brisk and efficient. “We’ve received sixteen applications for grazing permit modifications in the past month alone. Ranchers requesting emergency adjustments to traditional rotation schedules because of drought conditions. Your job is helping us evaluate which modifications are scientifically sound and which ones might cause long-term damage.”
The office activity that felt different from university settings. No one was laughing or even smiling. Maps covered every available wall surface, marked with colored pins showing active projects, pending permits, and areas of concern.
Diana paused beside a large topographical map, her finger tracing boundaries marked in red. “See this area? Three generations of the Morrison family—no relation to Jack in fire dispatch—have run cattle there using rotation patterns established by the grandfather. Now they’re requesting permission to graze areas that were off-limits during drought years.”
She turned to face Mia directly. “Problem is, those off-limits areas are the seed source for recovery. Use them now, we might solve this year’s crisis while creating next decade’s catastrophe.”
Across the building, Sam was meeting Jack Morrison, a lean man whose sun-weathered face and calm demeanor suggested someone comfortable with high-pressure decision making. Morrison’s office contained multiple computer screens displaying real-time weather data, satellite imagery, and communication equipment that connected him to fire crews across the region.
“First thing you need to understand,” Morrison said, settling behind his desk while gesturing toward a large monitor displaying current drought conditions, “is that everything we thought we knew about fire behavior is changing. Fuel loads, humidity levels, wind patterns, temperature extremes—all the variables we use for prediction models are shifting.”
Red zones dominated the display, indicating extreme drought conditions. Morrison’s weather-beaten hands moved across his keyboard with surprising dexterity, pulling up additional data layers.
“Your job this summer is helping us adapt our response protocols to new realities. Traditional fire season used to run from July through September. Now it’s April through November.” He paused, looking directly at Sam. “That’s not just a longer season—it’s a completely different operational framework.”
Morrison leaned back in his chair, studying Sam’s expression. “Had a crew leader tell me yesterday that fighting fires now feels like playing chess against an opponent who changes the rules mid-game. Twenty years of experience counting for less each season.”
By lunch time, both Mia and Sam had been immersed in briefings that revealed the complexity of their assignments. They met in the building’s small break room, comparing notes while eating lunches they’d been advised to pack.
“Diana showed me grazing permit applications from ranchers requesting permission to use traditionally protected areas,” Mia said, unwrapping a sandwich. “Areas that were set aside to preserve native plant communities during drought periods. But the drought is so severe that even the protected areas might be the only viable option for maintaining livestock operations.”
Sam nodded grimly, his own lunch untouched. “Morrison’s dealing with similar impossible choices. We have half the firefighting resources we need, fuel conditions that are dangerously extreme, and weather patterns that render prediction models useless. He said they’re essentially improvising solutions in real-time.”
The weight of responsibility was settling over them. Through the break room window, they could see the district’s fleet of emergency vehicles, each one representing someone’s safety and livelihood.
“I keep thinking about Dr. Martinez’s comment concerning fresh perspectives,” Mia said, taking a sip of water that did little to ease her dry throat. “What if our lack of experience is actually valuable?” The situation so incongruous the two graduate trainees shared amused expressions. “We’re not invested in traditional approaches that might not work anymore.”
“That’s simultaneously terrifying and inspiring,” Sam replied, finally taking a bite of his sandwich.
A radio crackled to life down the hall, calling for units to investigate a smoke report. Both students turned toward the sound instinctively, listening to voices coordinating a response. The casual lunch atmosphere gone for good.
“Gets easier,” said a voice from the doorway. They turned to see a woman in her fifties wearing the practical clothing of someone who spent considerable time outdoors. “The constant state of readiness, I mean. I’m Janet Martinez—no relation to your Dr. Martinez. Work vegetation surveys with Diana’s team.”
She poured coffee that looked like it had been brewing for hours. “Twenty-three years with BLM, and I’ve never seen conditions like this. But you learn to deal with uncertainty. Has to become normal, or you’d go crazy with worry.”
Janet studied them both with experienced eyes. “You’re the graduate students Diana and Jack have been bragging about. Good. We need people who understand that everything’s changing. Too many folks still trying to manage twenty-first-century problems with twentieth-century solutions.”
That evening, after their first full day of orientation and initial assignments, they walked together toward the parking lot. The setting sun painted the landscape in shades of gold and amber, beautiful in a way that hid the underlying stress conditions.
“Want to grab dinner? We should debrief today’s experiences. Compare observations.”
Mia smiled at his careful phrasing, recognizing her own uncertainty on how to navigate the transition from professional collaboration to personal interest. “Yes,” she said. “I think debriefing is essential.”
The restaurant they chose was quieter than their campus celebration diner, filled with locals who seemed to carry the day’s heat and stress in their postures. Conversations at nearby tables touched on water restrictions, fire danger ratings, and the economic impact of drought.
Over burgers and coffee, they processed their first day’s experiences.
“Diana mentioned that three major ranching operations in the district have sold their cattle,” Mia said, watching Sam’s face in the soft restaurant lighting. “That’s decades of careful breeding, family legacies, entire ways of life”
“As we expected, they’re seeing fire behavior that doesn’t match any historical patterns,” Sam replied, his voice dropping as he noticed other diners listening. “Fires moving faster, burning hotter, jumping traditional barriers like roads and rivers. Morrison mentioned one crew that had to deploy emergency shelters because their escape route was cut off by unexpected wind shifts.”
The weight of the day’s revelations settled between them. Around them, other conversations continued—complaints about utility bills, excitement for weekend plans, discussions of local politics—normal life proceeding while they grappled with evidence of accelerating environmental crisis.
“It’s strange,” Mia said, “how routine everything feels here while we’re dealing with what’s essentially an unfolding emergency. People are adapting so gradually that the change feels manageable, even though the cumulative impact is going to be enormous.”
Sam considered this while watching the restaurant’s evening crowd. A family at the corner table was celebrating a child’s birthday, their laughter bright against the subdued conversations elsewhere. “Maybe that’s how major changes always happen. Incrementally, until one day you look around and realize everything has shifted.”
“Can I tell you something?” Mia said as they prepared to leave. The restaurant had grown quieter, most diners heading home to prepare for tomorrow’s responsibilities. “Today was the first time my academic work felt genuinely important. Not just intellectually interesting or useful for career advancement, but actually meaningful.”
“I know exactly what you mean,” Sam replied, his hand briefly covering hers on the table. The contact was warm and welcome, lasting long enough to send its warmth spiraling through her before he pulled away. “We’re getting to work on serious problems.”
They walked to their cars through air that still held the day’s heat and the western horizon maintained a faint glow from the sun’s passage. The sound of their footsteps echoed off the asphalt, creating an intimate pocket of shared space.
“Same time tomorrow?” Sam asked as they reached her car, and Mia realized he was asking about more than their work schedules.
“Yes,” she said, feeling certainty settle in her chest like a small flame taking hold. When he leaned closer to say goodnight, she caught his scent—soap and sunscreen and something distinctly him that made her want to step closer rather than maintain professional distance.
As they drove home through darkness punctuated by distant lightning that promised no relief from the drought, both carried the knowledge that whatever challenges emerged, they wouldn’t face them alone. Behind them, the BLM office building stood dark except for the communications center, where skeleton crews maintained watch over weather patterns and fire danger indicators that would shape tomorrow’s decisions.
In the distance, barely visible against the star-filled horizon, a thin column of smoke rose from what would become another battle in the most challenging fire season on record. But tonight, driving home with windows down and radio playing softly, they thought not of the work ahead but of the unexpected gift of finding someone who understood both the weight of meaningful work and the courage required to face an uncertain future with hope intact.
Love, like fire, could start with the smallest spark—but under the right conditions, both will transform entire landscapes.